08、环形链表2
题目描述
今天给大家介绍比较有特点的题目,也是一个特别经典的题目,判断链表中有没有环,并返回环的入口。
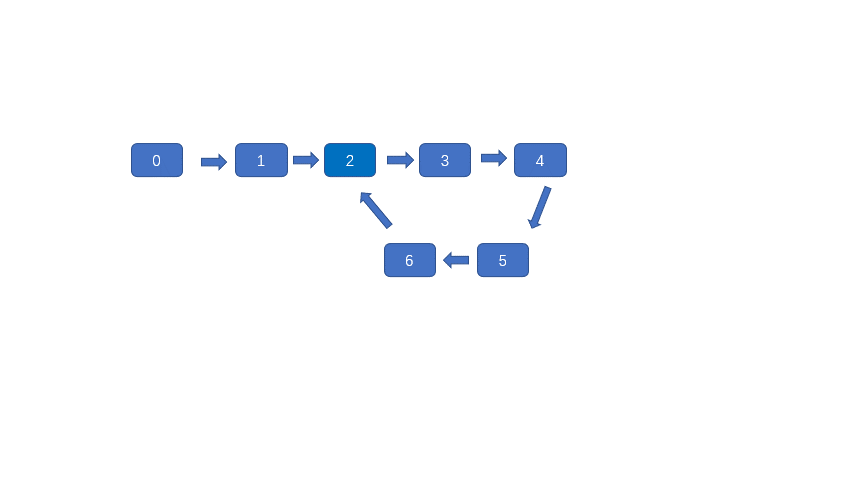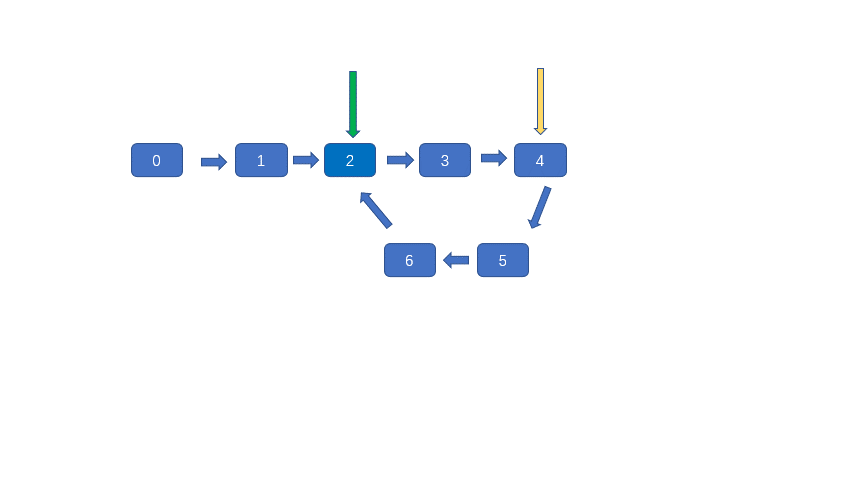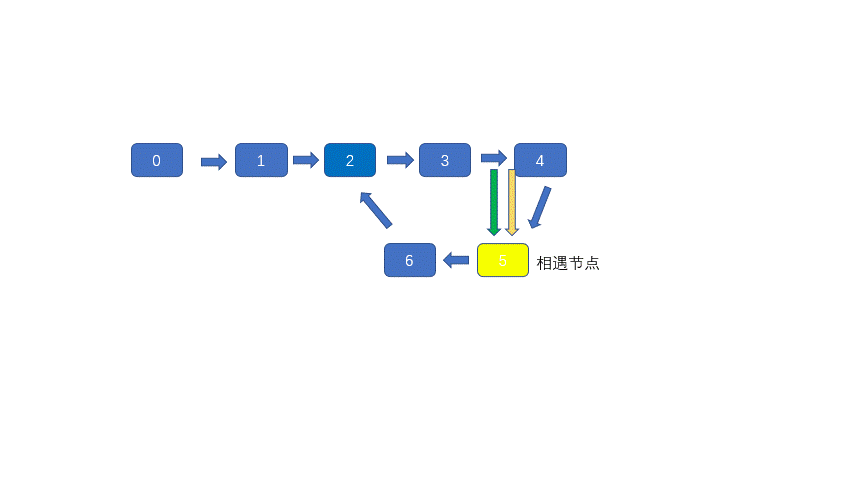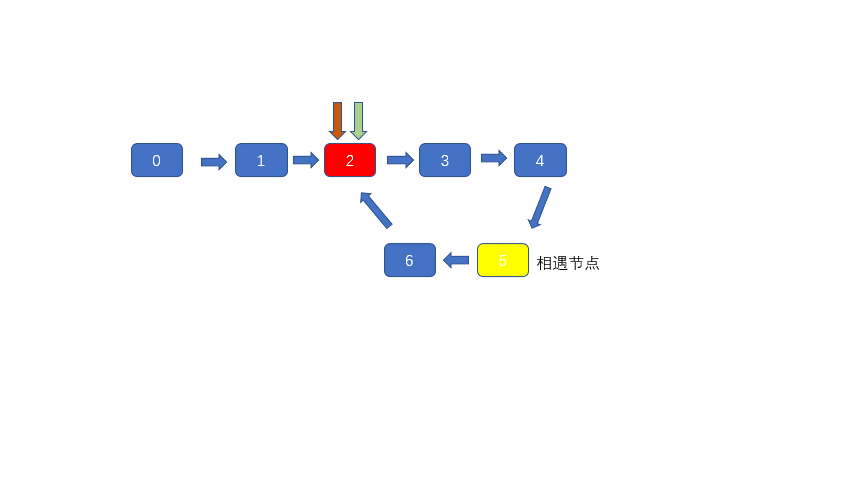
我们可以先做一下这个题目,就是如何判断链表中是否有环呢?下图则为链表存在环的情况。
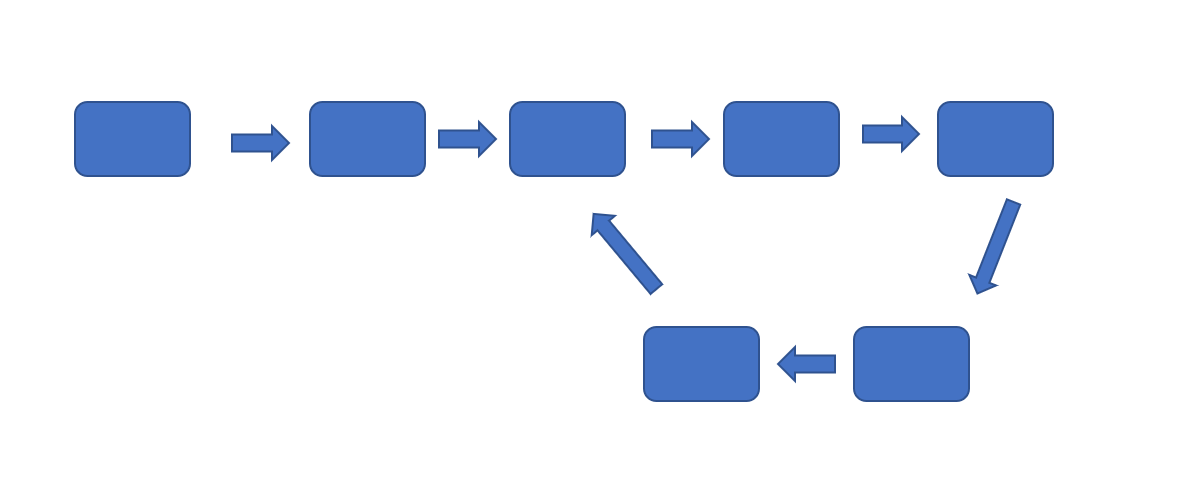
判断链表是否有环是很简单的一个问题,我们只需利用之前的快慢指针即可,大家想一下,指针只要进入环内就只能在环中循环,那么我们可以利用快慢指针,虽然慢指针的速度小于快指针但是,总会进入环中,当两个指针都处于环中时,因为移动速度不同,两个指针必会相遇。
我们可以这样假设,两个孩子在操场顺时针跑步,一个跑的快,一个跑的慢,跑的快的那个孩子总会追上跑的慢的孩子。
代码请参考之前的环形链表1
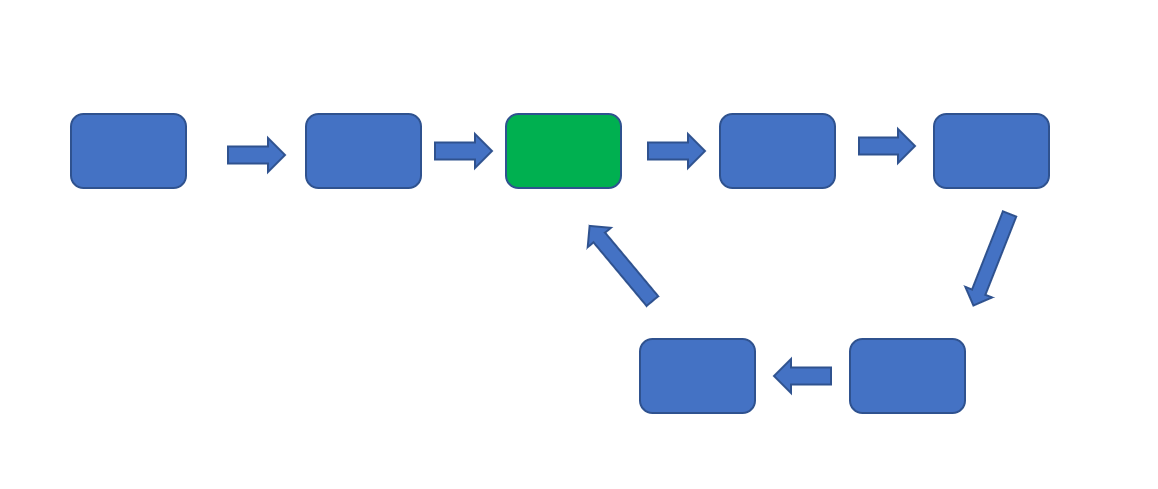
判断链表是不是含有环很简单,但是我们想找到环的入口可能就没有那么容易了。(入口则为下图绿色节点)
然后我们返回的则为绿色节点的索引,则返回 2。
HashSet
题目解析
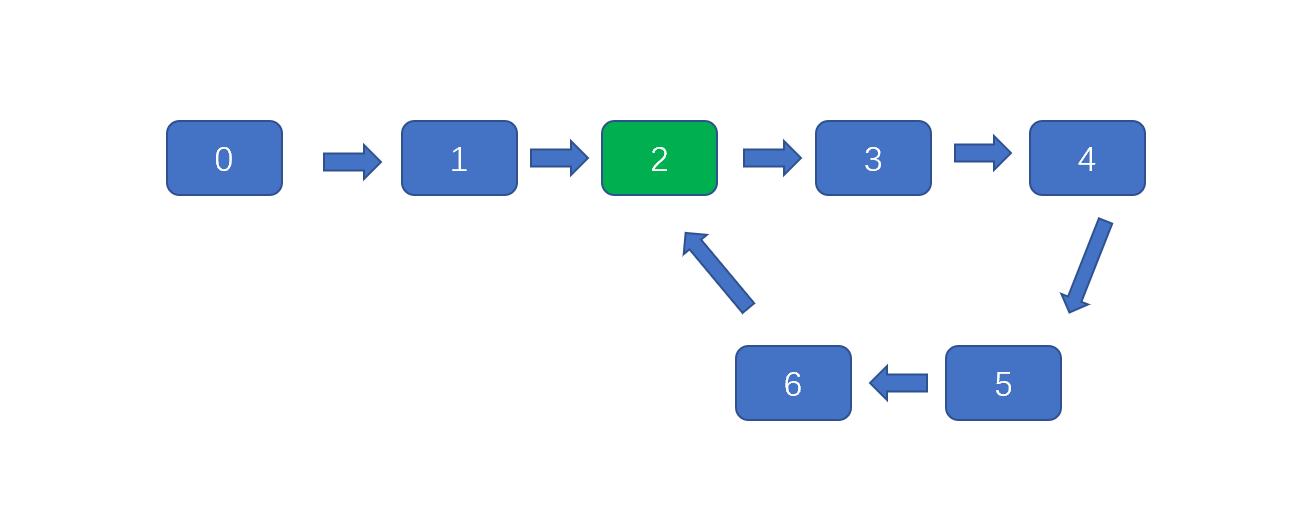
我们可以利用 HashSet 来做,之前的文章说过 HashSet 是一个不允许有重复元素的集合。所以我们通过 HashSet 来保存链表节点,对链表进行遍历,如果链表不存在环则每个节点都会被存入环中,但是当链表中存在环时,则会发重复存储链表节点的情况,所以当我们发现 HashSet 中含有某节点时说明该节点为环的入口,返回即可。
下图中,存储顺序为 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,**2 **因为 2 已经存在,则返回。
代码
Java Code:
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
if (head.next == null) {
return head.next;
}
//创建新的HashSet,用于保存节点
HashSet<ListNode> hash = new HashSet<ListNode>();
//遍历链表
while (head != null) {
//判断哈希表中是否含有某节点,没有则保存,含有则返回该节点
if (hash.contains(head)) {
return head;
}
//不含有,则进行保存,并移动指针
hash.add(head);
head = head.next;
}
return head;
}
}
C++ Code:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (head == nullptr) return head;
if (head->next == nullptr) return head->next;
//创建新的HashSet,用于保存节点
set<ListNode *> hash;
//遍历链表
while (head != nullptr) {
//判断哈希表中是否含有某节点,没有则保存,含有则返回该节点
if (hash.count(head)) {
return head;
}
//不含有,则进行保存,并移动指针
hash.insert(head);
head = head->next;
}
return head;
}
};
快慢指针
题目解析
这个方法是比较巧妙的方法,但是不容易想到,也不太容易理解,利用快慢指针判断是否有环很容易,但是判断环的入口就没有那么容易,之前说过快慢指针肯定会在环内相遇,见下图。

上图黄色节点为快慢指针相遇的节点,此时
快指针走的距离:a+(b+c)n+b,n 代表圈数。
很容易理解 b+c 为环的长度,a 为直线距离,b 为绕了 n 圈之后又走了一段距离才相遇,所以相遇时走的总路程为 a+(b+c)n+b,合并同类项得 a+(n+1)b+nc。
慢指针走的距离:a+(b+c)m+b,m 代表圈数。
然后我们设快指针得速度是慢指针的 2 倍,含义为相同时间内,快指针走过的距离是慢指针的 2 倍。
**a+(n+1)b+nc=2[a+(m+1)b+mc]整理得a+b=(n-2m)(b+c),**那么我们可以从这个等式上面发现什么呢?
b+c为一圈的长度。也就是说 a+b 等于 n-2m 个环的长度。为了便于理解我们看一种特殊情况,当 n-2m 等于 1,那么 a+b=b+c 整理得,a=c。此时我们只需重新释放两个指针,一个从 head 释放,一个从相遇点释放,速度相同,因为 a=c 所以他俩必会在环入口处相遇,则求得入口节点索引。
算法流程:
1.设置快慢指针,快指针速度为慢指针的 2 倍。
2.找出相遇点。
3.在 head 处和相遇点同时释放相同速度且速度为 1 的指针,两指针必会在环入口处相遇。
代码
Java Code:
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
//快慢指针
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
//设置循环条件
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
//相遇
if (fast == slow) {
//设置一个新的指针,从头节点出发,慢指针速度为1,所以可以使用慢指针从相遇点出发
ListNode newptr = head;
while (newptr != slow) {
slow = slow.next;
newptr = newptr.next;
}
//在环入口相遇
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
}
C++ Code:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
//快慢指针
ListNode * fast = head;
ListNode * slow = head;
//设置循环条件
while (fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
//相遇
if (fast == slow) {
//设置一个新的指针,从头节点出发,慢指针速度为1,所以可以使用慢指针从相遇点出发
ListNode * newnode = head;
while (newnode != slow) {
slow = slow->next;
newnode = newnode->next;
}
//在环入口相遇
return slow;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};