06、合并两个排序的链表
大约 3 分钟数据结构算法算法基地面试链表双指针递归刷题程序厨校招社招
题目描述
合并两个排序的链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
今天的题目思路很简单,但是一遍 AC 也是不容易的。链表大部分题目考察的都是考生代码的完整性和鲁棒性,所以有些题目我们看着思路很简单,但是想直接通过还是需要下一翻工夫的,所以建议大家将所有链表的题目都自己写一下。实在没有时间做的同学,可以自己在脑子里打一遍代码,想清每一行代码的作用。
迭代法:
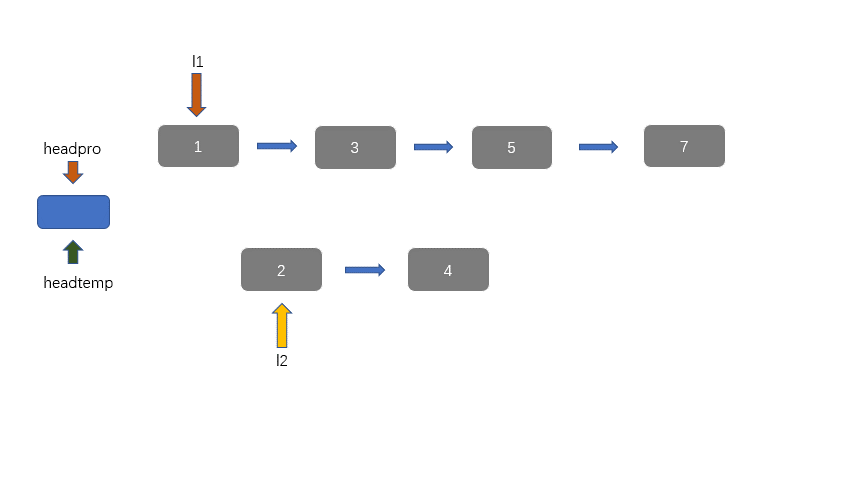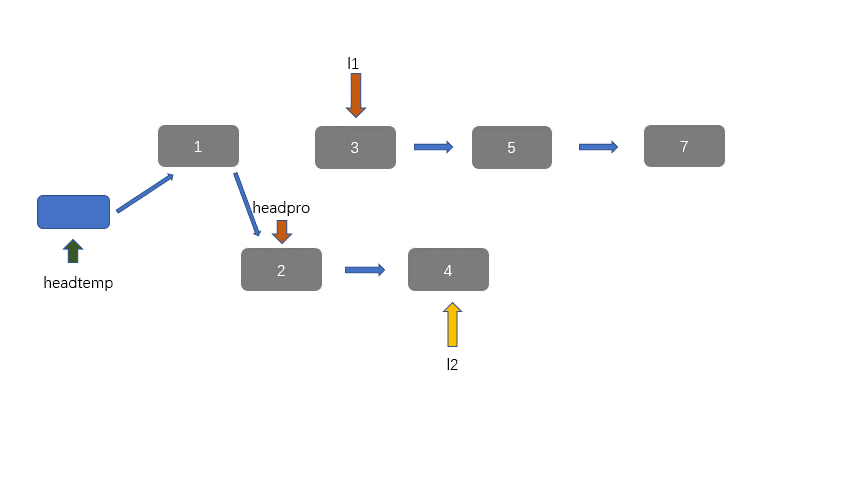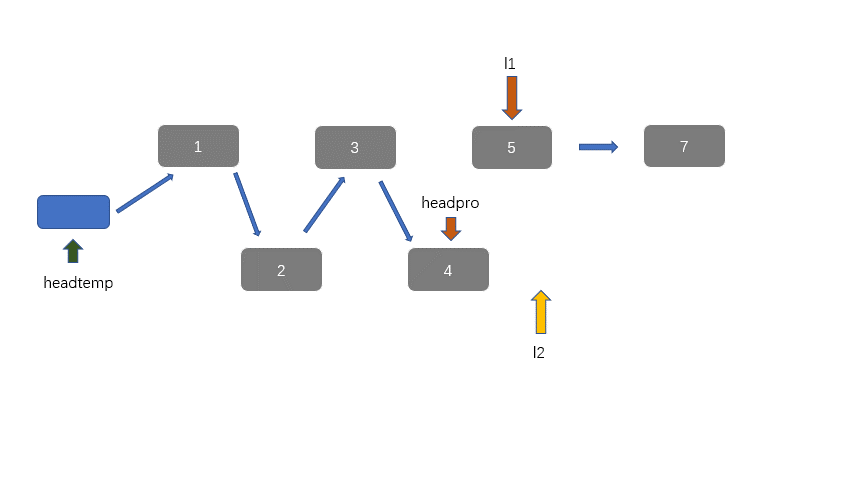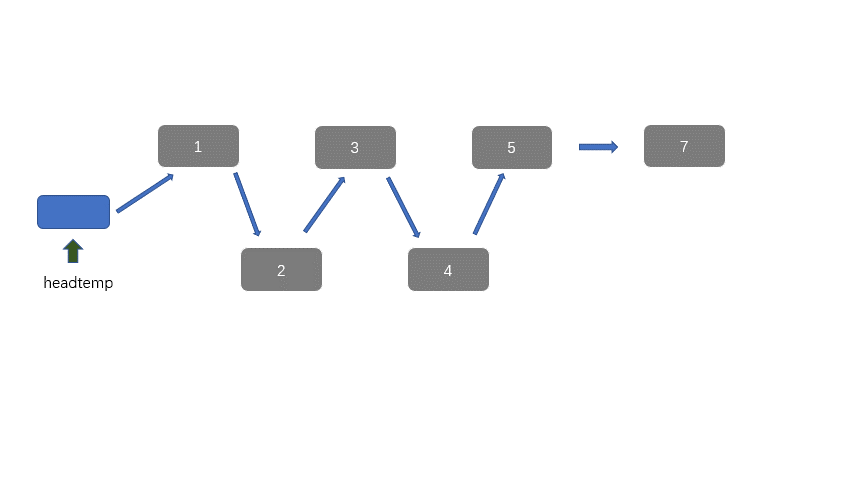
因为我们有两个升序链表,我们需要将其合并,那么我们需要创建一个新节点 headpre,然后我们利用双指针思想,每个链表放置一个指针,然后进行遍历并对比当前指针指向的值。然后 headpre.next 指向较小值的那个节点,不断迭代,直至到达某一有序链表底部,此时一个链表遍历完成,然后我们将未完全遍历的链表接在我们接在合并链表之后即可。
这是我们迭代做法,另外这个题目还有一个递归方法,目前先不写,等链表掌握差不多的时候会单独写一篇关于递归的文章,也算是为树的题目做铺垫。
动图讲解
代码
Java Code:
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode headpro = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode headtemp = headpro;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
//接上大的那个
if (l1.val >= l2.val) {
headpro.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
else {
headpro.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}
headpro = headpro.next;
}
headpro.next = l1 != null ? l1:l2;
return headtemp.next;
}
}
C++ Code:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode * headpro = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode * headtemp = headpro;
while (l1 != nullptr && l2 != nullptr) {
//接上大的那个
if (l1->val >= l2->val) {
headpro->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
else {
headpro->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
headpro = headpro->next;
}
headpro->next = l1 != nullptr ? l1: l2;
return headtemp->next;
}
};